For hardware hackers, boards like Arduino and Raspberry Pi are the essential building blocks that let them mix and mash things together. But while these devices don’t have the processing power to run our core tracking software, there are many ways to bridge hand tracking input on your computer with the Internet of Things. You’ll just need to interface the computer running the Leap Motion software with your favorite dev board!
In this post, we’ll look at a couple of platforms that can get you started right away, along with some other open source examples. This is by no means an exhaustive list – Arduino’s website features hundreds of connective possibilities, from different communication protocols to software integrations. Whether you connect your board directly to your computer, or send signals over wifi, there’s always a way to hack it.
Platform Integrations
Wireless Control with Cylon.js
For wireless-enabled controllers, it’s hard to beat the speed and simplicity of a Node.js setup. Cylon.js takes it a step further with integrations for (deep breath) Arduino, Beaglebone, Intel Galileo and Edison, Raspberry Pi, Spark, and Tessel. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg, as there’s also support for various general purpose input/output devices (motors, relays, servos, makey buttons), and inter-integrated circuits.
On our Developer Gallery, you can find a Leap Motion + Arduino example that lets you turn LEDs on and off with just a few lines of code. Imagine what you could build:
"use strict";
var Cylon = require("cylon");
Cylon.robot({
connections: {
leap: { adaptor: "leapmotion" },
arduino: { adaptor: "firmata", port: "/dev/ttyACM0" }
},
devices: {
led: { driver: "led", pin: 13, connection: "arduino" }
},
work: function(my) {
my.leapmotion.on("frame", function(frame) {
if (frame.hands.length > 0) {
my.led.turnOn();
} else {
my.led.turnOff();
}
});
}
}).start();
Visual Scripting with Vuo
Vuo is a visual scripting platform that features the ability to connect a wide variety of inputs and outputs. The latest version includes support for Serial I/O, which opens up access to a range of devices, including Arduino boards. Read more about Vuo in our featured blog post or learn more from their feature request thread.
Open Source Examples
Arduino + 3D Printer
This Processing sketch from Andrew Maxwell-Parish lets you control a Makerbot 3D printer with hand movements. It works by gathering the XYZ position of your fingers from the Leap Motion API, converting it into the Cartesian coordinates needed for the 3D printer, packaging it into G-code format, and sending it to the printer via an Arduino-based controller.
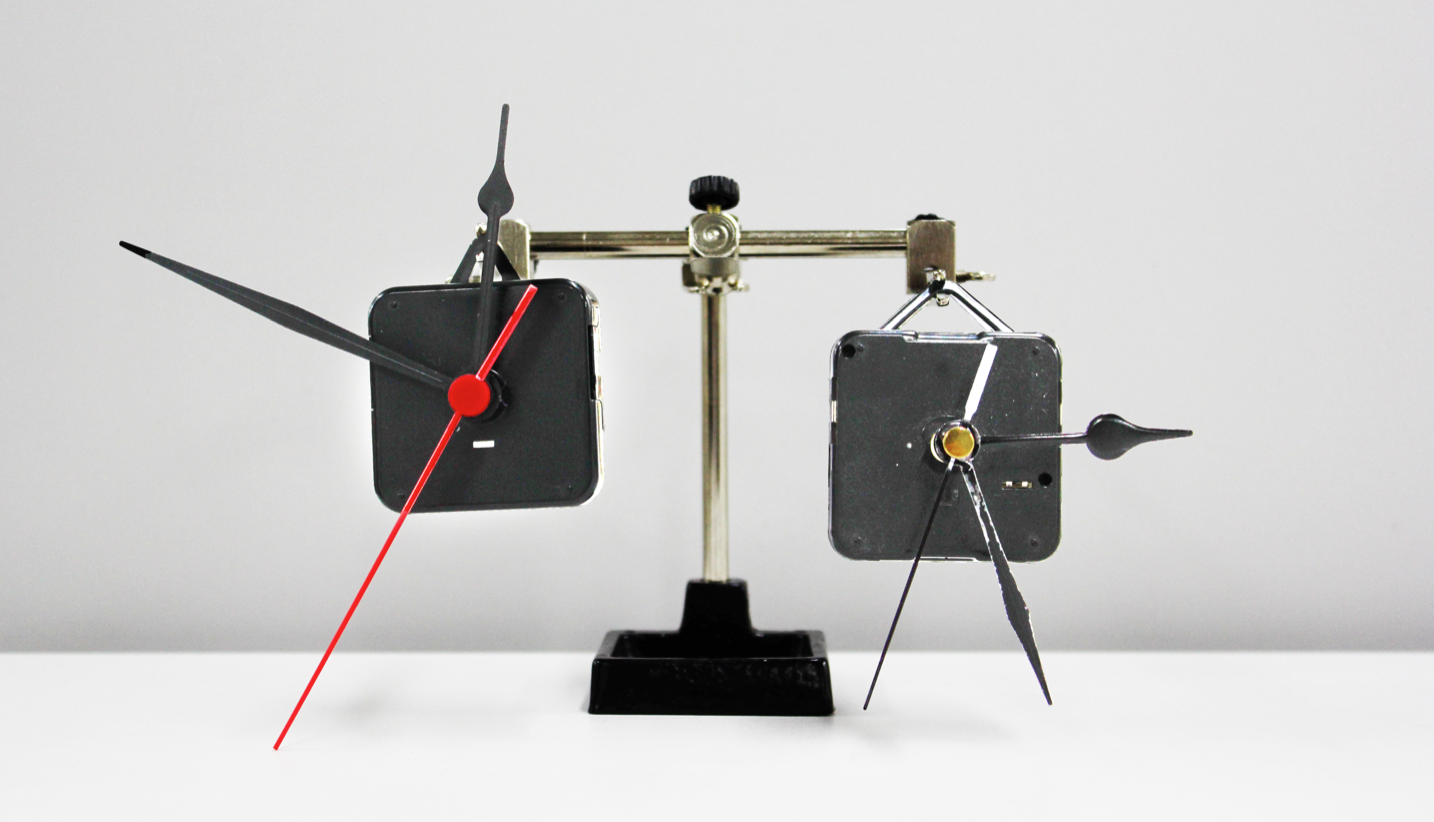
Arduino Motor Shield + Clock Motors
The Arduino Motor Shield is an additional kit that makes it easy for you to control motor direction and speed with your Arduino. (Check out this great Instructables tutorial to set it up.) Using the Motor Shield and a Processing script, interactive design student James Miller created BLAST: Time – a little sculpture with a clock that responds to people’s hand movements.
Robotic Arm
Built in Python, this award-winning hack from last year’s LA Hacks featured a robotic arm with five different motors. Leap Motion data was sent to the arm controller through a Bluetooth connection, allowing the team to place in the competition finals.

Hacking a Radio Drone
When it comes to DIY robotics, taking the sneaky route is often half the fun. Using an Arduino-to-radio interface, another LA Hacks team was able to hack a drone’s radio signal, taking control from analog to digital. According to hardware hacker Casey Spencer, “remote control through the Internet, computer-aided flight, or even – with a little more hardware – complete autonomy is now possible for the majority of consumer drones already out there.”
Are you using Leap Motion interaction to help trigger the robo-apocalypse? Let us know in the comments, or share your project on the community forums!







[…] For hardware hackers, boards like Arduino and Raspberry Pi are the essential building blocks that let them mix and mash things together. […]
June 20, 2015 at 1:23 am[…] How to Integrate Leap Motion with Arduino & Raspberry Pi […]
June 21, 2015 at 4:39 am[…] I recently came across this article on the Leap Motion blog and thought it might serve as a good starting point for others. You can read the article here. […]
June 21, 2015 at 4:43 pm[…] with minimal coding. We’ve seen hundreds of Leap Motion experiments using Processing, from Arduino hacks to outdoor art installations, and the list grows every […]
June 25, 2015 at 1:05 pmI am trying to make 3d ar/vr glasses whit raspberry pi , a screen and leap motion.Can I use the leap motion as in windows or mac,can I make virtual reality
July 10, 2015 at 1:29 amThe Raspberry Pi doesn’t hit our minimum system requirements; you’d need to use a supported Android device using our Android SDK (currently in private alpha) or run the software on a Mac/PC.
July 13, 2015 at 5:23 amis there no way to get a pared down dataset sent to a Pi?
October 10, 2017 at 8:52 pmYou can run the Leap Motion software on a PC and then send the data to a Pi using Node.js or another library.
October 11, 2017 at 5:29 amLooks like no one has done this. Anyone know of a less computationally intense alternative to Leap Motion? Hopefully I won’t have to create one from scratch…
October 11, 2017 at 6:29 am[…] our blog, we cover a couple of platforms that can get you started right away (along with some open source […]
September 21, 2015 at 8:58 amhow many arduino controllers can a single raspberry-pi or pine64 handle?
February 1, 2016 at 12:45 pm[…] Como integrar con Arduino y Raspberry Pi: http://blog.leapmotion.com/integrate-leap-motion-arduino-raspberry-pi/ […]
September 7, 2016 at 7:21 amCan we directly connect raspberry pi and leap motion controller? I saw that there is ARM-9 used inbetween them.
November 14, 2016 at 12:53 amThe Processing sketch is unavailable for download, can you upload one more time?
April 15, 2017 at 8:27 am[…] post from leapmotion "How to Integrate Leap Motion with Arduino & Raspberry Pi" […]
December 26, 2017 at 8:55 am[…] our blog, we cover a couple of platforms that can get you started right away (along with some open source […]
January 8, 2018 at 7:30 am